Géométrie dans l'espace
Intersection de plans et de droites dans l'espace
Intersection de deux plans
Propriété
Soit -
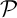 et
et  sont strictement parallèles: ils
n'ont aucun point commun
sont strictement parallèles: ils
n'ont aucun point commun
-
 et
et 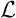 sont sécants suivant une droite
sont sécants suivant une droite 
-
 et
et  sont confondus: leur intersection
est un plan
sont confondus: leur intersection
est un plan
(3,0)(4,1)(1,1)](Cours-IMG/499.png)
Propriété
Algébriquement,
si les plans ![\[\la\bgar{ccccccccc}
ax &+& by &+& cz &+& d &=& 0\\
a'x &+& b'y &+& c'z &+& d'&=& 0
\enar\right.\]](Cours-IMG/505.png)
Si les plans sont sécants (cas 2.), le système est alors un système d'équations cartésiennes représentant la droite

Remarque: dans l'espace une équation cartésienne décrit un plan. Pour décrire une droite, il faut deux équations cartésiennes.
Exercice 18
- Le système
![\[\la\bgar{rccccrrcc}
2x &-& y &+& 3z &-& 1 &=& 0\\
x &+& y &-& 4z &-& 6&=& 0
\enar\right.\]](Cours-IMG/508.png)
est-il un système d'équations cartésiennes d'une droite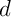 ?
?
- Déterminer
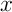 et
et 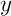 en fonction de
en fonction de 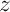 , puis en déduire une équation
paramétrique de
, puis en déduire une équation
paramétrique de 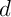 , en introduisant le paramètre
, en introduisant le paramètre 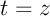 .
.
Donner alors un point et un vecteur directeur de .
.
Exercice 19
Dans un RON, les plans et
Etudier l'intersection des plans
Intersection d'une droite et d'un plan
Propriété
Soit -
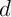 et
et  sont strictement parallèles: ils
n'ont aucun point commun
sont strictement parallèles: ils
n'ont aucun point commun

-
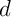 et
et 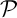 sont sécants en un unique point
sont sécants en un unique point 

-
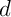 est contenue dans
est contenue dans  : leur intersection
est la droite
: leur intersection
est la droite 
Exercice 20
Dans un RON, le plan ![\[\la\bgar{ll}
x=t\\
y=1-6t \\
z=3-t
\enar\right.,\ t\in\R\]](Cours-IMG/574.png)
Déterminer l'intersection de
Exercice 21
Les points Etudier l'intersection de la droite
Intersection de trois plans
Voir aussi: